On this webpage you will find the following information:
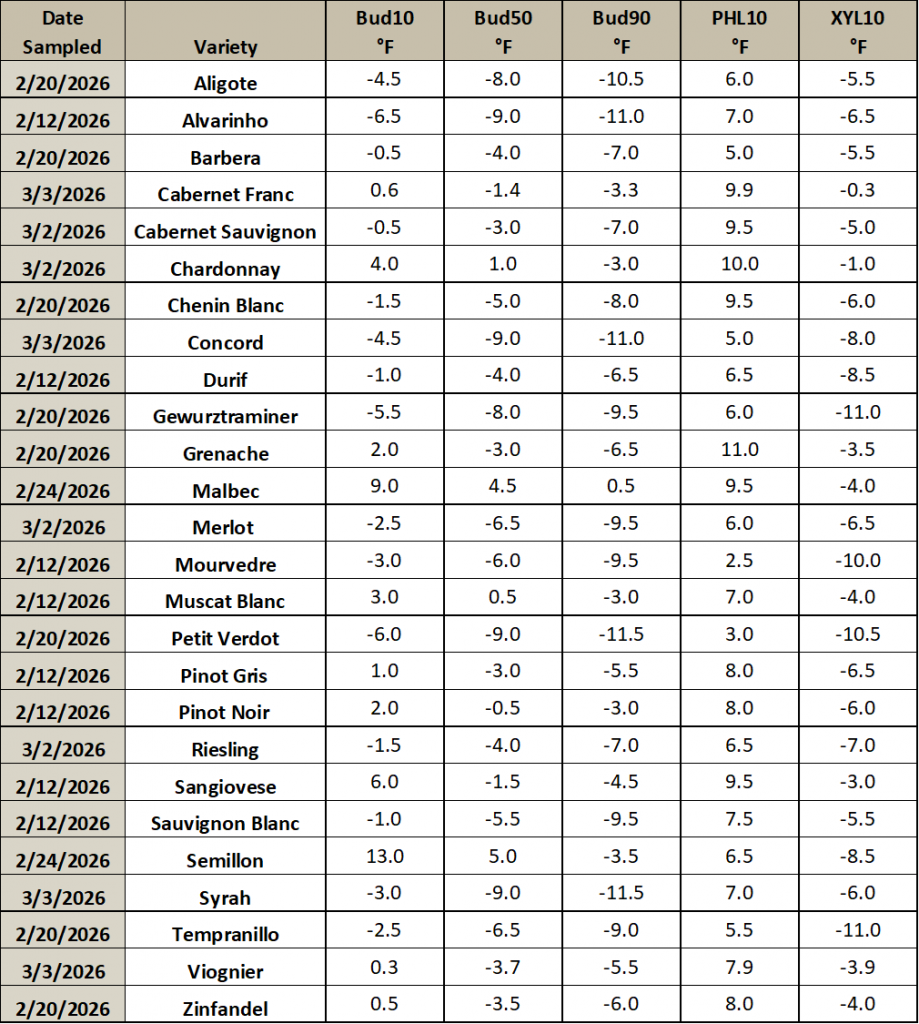
- Real-Time Monitoring – This is a table of actual measured cold hardiness for specific varieties grown at WSU Prosser IAREC. Updated weekly to bi-weekly.
- Variety Graphs – A variety-specific seasonal overview of cold hardiness over time.
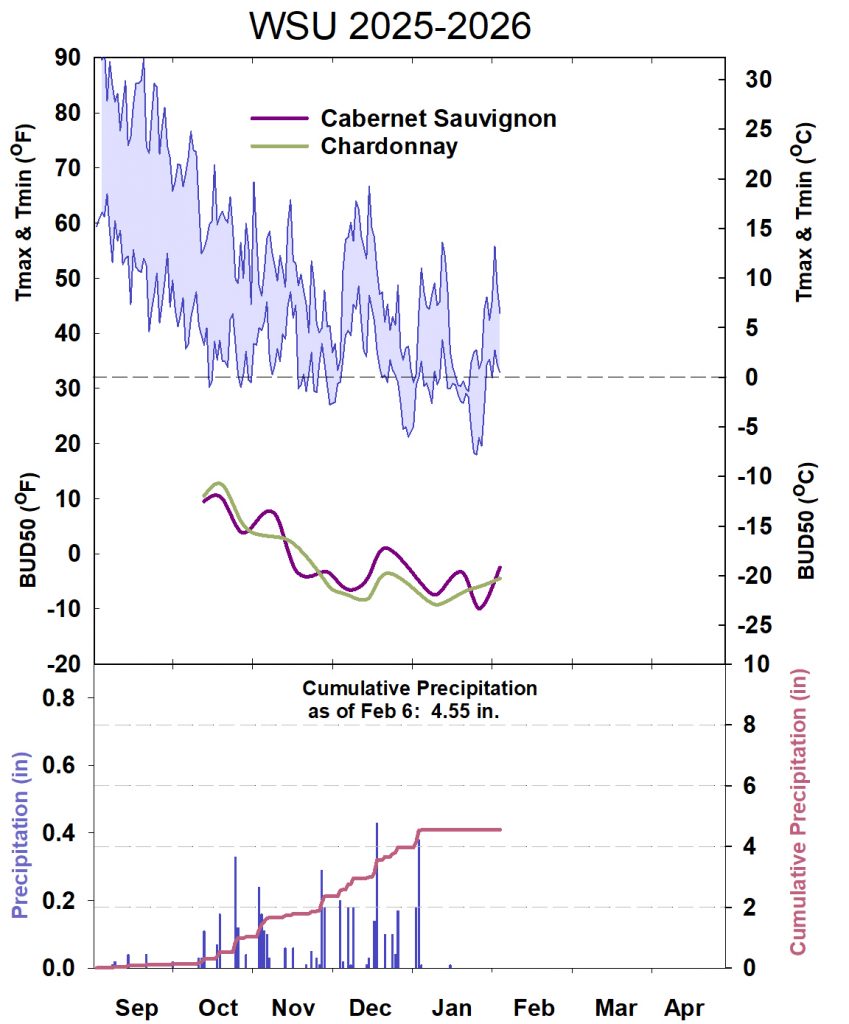
- Seasonal Summary – A general overview of temperatures and precipitation, along with cold hardiness, for Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay.
- Initial Fall Cold Hardiness, Potential Maximum Cold Hardiness in mid-Winter, and Spring Frost tolerance of select varieties. This is data summarized from our historical monitoring.
Real-Time Monitoring
Resources
Preventing Cold Damage in Grapes:
- Grapevine Training Systems for Managing Winter Cold Injury – OSU #EM9432
- 2012 USDA Plant Hardiness Zones
Assessing Cold Damage in Grapes:
- Assessing and Managing Cold Damage in Washington Vineyards – WSU #EM042E
- Anatomy of Winter Injury (PDF) – Cornell University
Responding to Cold Damage in Grapes:
- Effect of Pruning on Recovery and productivity of Cold-Injured Merlot Grapevines – AJEV 2007 58:351-357
- Vine and Vineyard Management Following Low Temperature Injury – ASEV 2000 Cold Hardiness Workshop
Variety Graphs
Seasonal Summary
In the Spring
When we are at or approaching bud break, we can no longer run exotherm analysis in grapes. Below are some general guidelines as to the critical temperatures for cold damage for Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Chardonnay during the period leading up to bud break. Every variety responds differently to cold temperatures, so these are for guidelines only.
- Cabernet Sauvignon at budswell sustained no damage down to 25°F.
- Merlot at budswell showed slight damage to the buds, phloem, and xylem at 25°F. More serious damage to the phloem and xylem occurred at 23°F.
- Chardonnay at budswell to budbreak showed slight damage to the buds and phloem at 27°F. More serious phloem and xylem damage occurred at 25°F. Buds were seriously affected at 24°F.
Initial Cold Hardiness, Maximum Cold Hardiness, and Spring Frost Tolerance
The below table shows initial fall cold hardiness (mid-September) and potential maximum mid-winter cold hardiness for grapevine buds. It also shows frost tolerance of green tissue in the spring following budbreak.
Information is modified from Table 4 in Ferguson et al., 2014 (AJEV).
Variety |
Initial Fall Cold Hardiness(°F) |
Potential Maximum Mid-Winter Cold Hardiness(°F) |
Frost Cold Tolerance- Post Budbreak(°F) |
| Barbera | 13.8 | -10.3 | 29.8 |
| Cabernet franc | 14.2 | -13.7 | 29.8 |
| Cabernet Sauvignon | 13.5 | -13.2 | 29.8 |
| Chardonnay | 10.8 | -14.3 | 29.8 |
| Chenin blanc | 10.2 | -11.4 | 29.8 |
| Concord | 9.0 | -21.1 | 27.5 |
| Dolcetto | 13.8 | -9.8 | 29.8 |
| Gewurztraminer | 11.1 | -12.8 | 29.8 |
| Grenache | 14.0 | -8.9 | 29.8 |
| Lemberger | 8.6 | -14.1 | 29.8 |
| Malbec | 11.3 | -13.2 | 29.8 |
| Merlot | 13.5 | -13.0 | 29.8 |
| Mourvedre | 14.9 | -7.8 | 29.8 |
| Nebbiolo | 12.0 | -11.9 | 29.8 |
| Pinot gris | 10.4 | -11.4 | 29.8 |
| Riesling | 9.3 | -15.0 | 29.8 |
| Sangiovese | 12.7 | -7.4 | 29.8 |
| Sauvignon blanc | 12.9 | -12.8 | 29.8 |
| Semillon | 13.3 | -8.3 | 29.8 |
| Sunbelt | 10.8 | -20.4 | 27.5 |
| Syrah | 13.5 | -11.6 | 29.8 |
| Viognier | 11.8 | -11.2 | 29.8 |
| Zinfandel | 13.3 | -11.9 | 29.8 |
Modeling
Washington State University has developed a Cold Hardiness Model to predict grapevine cold hardiness anywhere temperature data is available. It is available both as an EXCEL sheet (to enter your own weather data), or via AgWeatherNet (for WA locations).
For the EXCEL version: Send your name, affiliation (Government, University, Grower, Consultant, Student), and location (City, State/Province, Country), in an email to: wsu.vitcoldhardiness@gmail.com
Please use “Cold Hardiness Model Request” as the subject line. You will receive an automate reply which will contain a link to download the file. We are asking for your contact information so that we may track where the model is being used.

